Teflon
Teflon, also known as Polytetrafluoroethylene, abbreviated as PTFE, (commonly known as "Plastic King, Harrah"), is a synthetic fluoropolymer discovered by Roy Plunkett. He has been researching new refrigerants and trying to find a new non-toxic alternative to sulfur dioxide and ammonia at DuPont. In fact, Teflon was discovered entirely by accident.
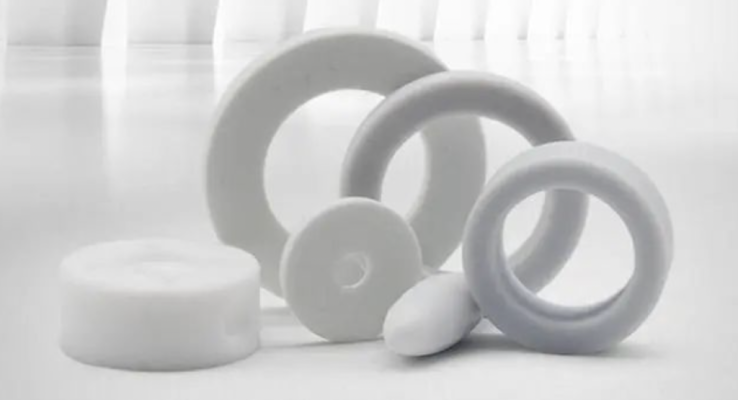
Teflon is a fluorocarbon-based polymer with multiple strong carbon-fluorine bonds, thus making it highly resistant to various substances. As a nonstick coating, PTFE is widely used on pans and other cookware. In fact, due to the strength of the carbon-fluorine bond, Teflon coatings can also be applied in containers and piping systems for reactive or corrosive chemicals.
Manufacturing process of Teflon coated magnet
Advantages of Teflon coated magnets
ü Non-stick performance.
ü Low friction coefficient: The friction coefficient of Teflon coated magnet is less than 0.1, only behind the diamond.
ü Moisture resistance: The surface of the PTFE coating film is not stained with water and oil, and it is not easy to stain with solution during production and operation. If there is a small amount of dirt, it can be removed by simply wiping. Short downtime saves man-hours and improves work efficiency.
ü High temperature resistance. Teflon coating can work continuously at high and low temperatures, can withstand high temperatures up to 300°C for a short time, and can be used continuously between 240°C and 260°C in general. It has remarkable thermal stability, and it can work at freezing temperatures Not brittle, does not melt at high temperatures.
ü Wear resistance: under high load, it has excellent wear resistance. 6. Chemical resistance: PTFE coated magnets have excellent acid and alkali resistance without pinholes.
Zinc coatings
The standard electrode potential of zinc is -0.76V/SHE, so zinc coatings are often used as sacrificial anodes for steel components. Zinc coatings can be obtained by various processes, and the permanent magnet industry has used electro-galvanization to protect neodymium magnets for a long time.
The potential of zinc is lower than that of hydrogen under aqueous conditions, so the electroplating of zinc in aqueous solution requires the participation of complexing agents.
Cyanide galvanizing has been replaced by other processes due to environmental concerns, and bath formulations for electro galvanizing of neodymium magnets include chlorides, sulfates, and zincates. Zinc chloride galvanizing is currently the most commonly used process.
The relatively high current efficiency and relatively low bath voltage of zinc chloride coatings mean that zinc chloride coatings are more energy efficient than other galvanizing processes.
The main salts in zinc chloride coating bath formulations contain KCl, ZnCl2 and H3BO3. Additives in the formulation include surfactants and brighteners. Surfactants refine the grains of zinc coatings by changing the electrode potential and cathodic polarization. Aromatic aldehydes and aromatic ketones are used as whitening agents to enhance the brightness and smoothness of zinc coatings.
The chemical properties of zinc are very active, which determines that the zinc coating needs passivation treatment after electroplating. The zinc coating reacts with the passivating agent to form a dense chemical conversion film. According to the passivation effect, zinc coating can be divided into colored zinc and blue white zinc. Due to the strong carcinogenic effect, the hexavalent chromium process has been replaced by trivalent chromium.
For the colored zinc process, the zinc coating of the NdFeB magnet will gradually form a passivation film after reacting with the acidic components in the air, and the thickness and color of the passivation film will change with the storage time. Simple high chromium passivation formulations include chromic anhydride, H2SO4 and HNO3. When chromic anhydride dissolves in water, it will form chromic acid, and the anhydride has a certain polishing effect on its strong oxidizing properties. It should be noted that chrome-free passivation is the future trend of electro-galvanized NdFeB magnets.
ABS plastic lagging coating
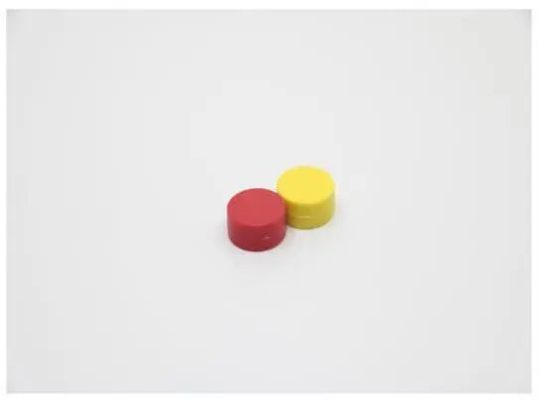
Plastic coated magnets are strong magnets, such as neodymium iron boron or ferrite, enclosed in a durable plastic housing. The natural rubber in rubber-coated magnets may have tiny pinholes and their performance may gradually deteriorate compared to plastic-coated magnets. At present, plastic-colored magnets are very popular in the market.
Production of plastic-coated magnets
In fact, the size of the plastic-coated magnet is generally standard size, and the plastic coating is made of ABS material. Injection molding machines will be used for mass production of plastic-coated magnets. For small batch customization requirements, 3D printing and ultrasonic plastic welding can be used to make samples, and then help customers save development costs.
The advantages of plastic-coated magnets
ü Completely waterproof
ü Benefiting from the closed structure, the plastic-coated magnet is safe to use in harsh environments, such as salt water and solution environments.
ü Due to the existence of plastic outside, the magnet will not break during use.
ü The plastic will also protect the surface of the magnetic whiteboard and refrigerator.
ü Colorful and individual appearance.
Application plastic-coated magnets
Currently, plastic-coated magnets are used in civilian applications. In fact, it has broad prospects in many fields. Plastic type and strength can be adjusted according to customer requirements.