Introduce Magnetic Disk Couplings.
Torque may be transferred without touch using magnetic couplings. To prevent corrosive, poisonous, or combustible substances from leaking into the atmosphere, they are often utilized in pumps for seal-less applications. Simple Concept: Opposite Poles Attract.
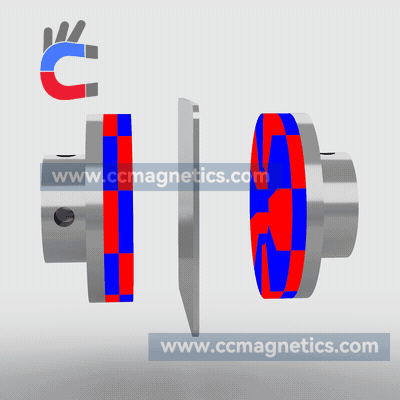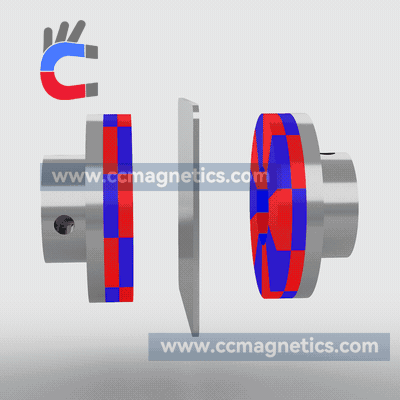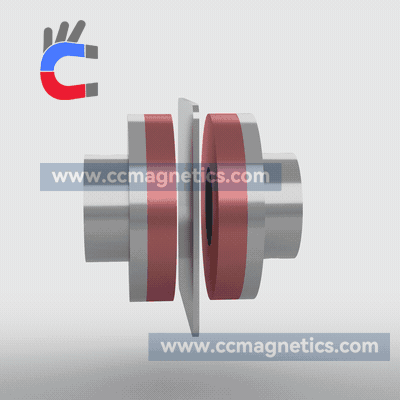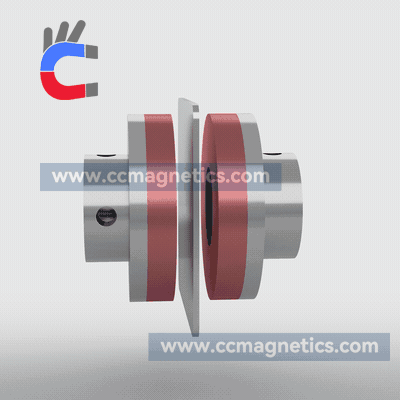
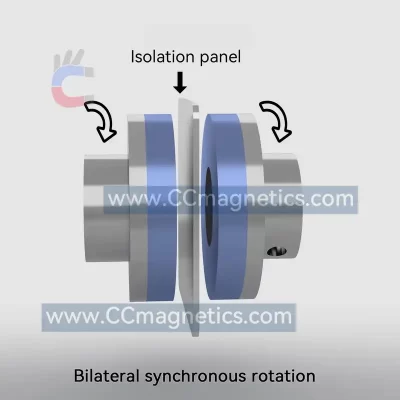
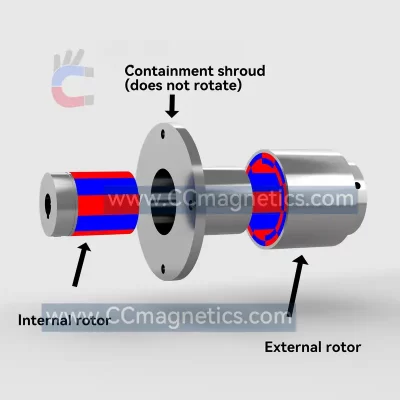
Magnetic disk couplings transfer torque from one magnetic hub to another via this attraction. Torque is transferred magnetically to the other magnetic hub by driving the first magnetic hub. The inner magnetic hub may be completely isolated from the outer magnetic hub by doing this via the air or a non-magnetic containment barrier like stainless steel or fiberglass. No contacting components exist.
Disc-type couplings have two opposed discs that are strongly magnetized using rare earth elements. Through an air gap, the second disc receives the torque given to the first disc. Due to its straightforward flat design, you can transfer virtually all of the rotating torque with angular misalignment up to 3º and parallel misalignment up to ¼”. You may also create a low-cost flat barrier to divide the fluids or atmospheres around the two discs. Our most straightforward and adaptable connection is this one.
Advantages of magnetic disk couplings
- No Wearing Components
- Design Synchronized, No Slip at Any Speed
- No physical contact between the parts that drive and are driven
- Containment Barrier Simplified
- Available Custom Designs
Disadvantages of magnetic disk couplings
Since the magnetic disk couplings rely on suction to transmit torque, the bracket that fixes the gear needs to withstand the suction and may deform over time.Therefore, for the protection of fixed brackets, magnetic shaft couplings will be better.